|
|
Post by Carol-Anne Lucero on Oct 29, 2015 12:08:39 GMT -7
Hi folks!
To help you and your teammates out with studying, I would like you to add terms and definitions of vocab words as you come across them in your studies. I want you to add 1-3 words to this list after every lesson. Occasionally I will assign specific tasks to contribute to this list, so stay tuned for more!
General format for replies:
Date of Lesson: Name of Lesson
word: definition
example)
|
|
|
|
Post by Example Student on Nov 6, 2015 12:29:10 GMT -7
EXAMPLE REPLY:
11/5: Anatomy Basics eponym: a name or noun formed after a person. eponym literally means 'above the name' (epi: above, nym: name). example) the golgi apparatus (also known as the golgi complex or golgi body) was named after Camillo Golgi after he was supposedly the first to discover it. -en.svg)
|
|
|
|
Post by Emily Drysdale on Nov 6, 2015 19:17:22 GMT -7
11/5: Anatomy Basics Cytoskeleton: a network of protein filaments and tubules within the cytoplasm of a cell. It is also used for movement of the cell as a whole and movement of organelles within the cell. Example) The cytoskeleton is used to transport organelles and chromosomes in the cells of the human body.  |
|
|
|
Post by Alexa Smith on Nov 10, 2015 22:18:28 GMT -7
11/5: Anatomy Basics
Macromolecules: The 4 classes of organic molecules that are vital to the functioning of life. They contain a lot of atoms, and thus are large molecules. They are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Example: Nucleic acids are used to make up DNA and RNA
|
|
|
|
Post by James Zheng on Nov 11, 2015 17:42:45 GMT -7
11/5: Anatomy Basics
Vestigial Structures: A structure in an organism that has lost all or most of its original function in the course of evolution.
Example: The human tailbone/coccyx is a vestigial structure.
|
|
|
|
Post by Aidan Brady on Nov 11, 2015 20:00:40 GMT -7
11/5: Anatomy Basics Eukaryote: any organism whose cells contain a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes. Example) All animal cells are eukaryotic. Nucleus: a dense organelle present in most eukaryotic cells, typically a single rounded structure bounded by a double membrane, containing the genetic material. 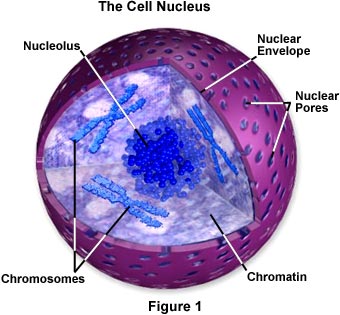 |
|
|
|
Post by Dylan Ellis on Nov 15, 2015 10:36:12 GMT -7
11/5: Anatomy Basics
osteoporosis: condition of fragile bones due to tissue loss
example) The elderly neighbor has developed osteoporosis because of age and a diet not meeting her calcium and Vitamin D needs.
|
|
|
|
Post by James Zheng on Nov 16, 2015 21:41:18 GMT -7
11/12: The Skin We're In
adipose tissue: loose connective tissue we know as fat; composed of adipocytes or fat cells & found in subcutaneous layer of skin
ex: Too much adipose tissue can lead to obesity!
|
|
|
|
Post by Dylan Ellis on Nov 16, 2015 22:31:19 GMT -7
11/12: The Skin We're In
Osgood-Schlatter Disease: repetitive use injury causing a painful lump under the patella
Example: Because the sport of basketball requires a lot of jumping, Osgood-Schlatter disease is very common in basketball players, especially those who played young.
|
|
|
|
Post by Natalie Spencer on Nov 18, 2015 8:13:22 GMT -7
Areolar connective tissue- loose, irregularly arranged connective tissue that consists of collagen and elastic fibers. Areolar connective tissue is found beneath the dermis, around mucous membranes, and blood vessels. Example: The areolar tissue surrounding Patty's blood vessels lost its elastic fibers and became immobile. Attachments:
|
|
|
|
Post by Alexa Smith on Nov 19, 2015 14:49:28 GMT -7
11/12: The Skin We're In
Melanocyte: cells in the stratum germinitivum layer that produce melanin, a pigment that helps protect cells from being mutated by UV rays.
Example: Bianca spent a lot of time in the sun, so her melanocytes produced a lot of melanin to protect her cells that made her appear tan.
|
|
|
|
Post by Alexa Smith on Nov 20, 2015 8:59:14 GMT -7
11/19: Integumentary Disorders
Herpes zoster virus: A virus that causes chicken pox. It remains in the body for life, and can come back as shingles in people who have had chicken pox.
Example: Edna and her daughter, Edith, both contracted the herpes zoster virus from a friend, and they both got chicken pox. Ten years later, Edna had a flare up of shingles.
|
|
|
|
Post by James Zheng on Dec 13, 2015 22:02:07 GMT -7
11/19: Integumentary Disorders
blackhead: a type of acne in which the hair follicle is plugged and excess sebum is released by the sebaceous gland; the black appearance is due to the exposure of the sebum to oxygen and thus the oxidation of the sebum
Example: I have a black pimple on my forehead, and the sebum is exposed to the air, so I have a blackhead.
whitehead: a type of acne in which the excess sebum released is not exposed to the air, creating a whitish appearance
Example: Don't pop whiteheads or blackheads!
|
|
|
|
Post by James Zheng on Dec 13, 2015 22:11:14 GMT -7
12/10: The Skeletal System: Your Body's Framework
osteoblast- a cell that helps with bone formation and works in a group with other osteoblasts (in osteons)
Example: When bone is continually replaced, osteoblasts help create the new bone to replace the old one that the osteoclasts took away.
osteoclast- a multinucleated cell that routinely breaks down bone matrix
Example: When bone is continually replaced, osteoblasts help create the new bone to replace the old one that the osteoclasts took away.
osteocyte- after an osteoblast has secreted bone matrix, it gets covered by its secretion to create a new cell called an osteocyte and becomes a part of the bone; sometimes secrete new bone matrix and influence the rate of bone remodeling
Example: After the osteoblast did its job, it "retired" and became an osteocyte.
|
|